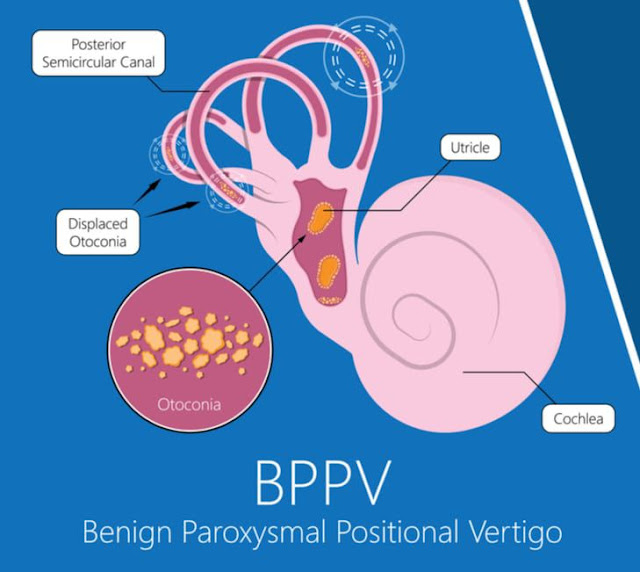
Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo, also known as BPPV, is a type of Vertigo which is by far the most common in Vertigo patients.
BPPV is caused by an inner ear issue, & leads patients to feel as if the room around them is spinning & their surroundings are moving even when they are perfectly still.
BPPV is usually not a serious condition, as the term Benign in its name specifies. It is usually triggered by certain head movements, as the term positional in the name suggests.
BPPV symptoms also hit suddenly & last for short bursts of time, as suggested by the term positional in its name.
If you have BPPV, you don’t need to worry at all. It is quite a common condition, & can be easily treated by a Vertigo doctor.
BPPV symptoms often resemble those of other conditions, & can be quite hard to diagnose at first.
BPPV is usually not fatal, unless it increases your chances of falling while performing certain activities like walking, jumping, mountain climbing, driving, weightlifting, etc.
BPPV Symptoms:
BPPV symptoms occur suddenly, & often makes the patient feel as if they’re spinning, moving, or about to fall down.
They are often triggered by a change in the position of the head, or any movement that can irritate the position of the calcium crystals misplaced inside the semicircular canal.
Some of the most common BPPV symptoms include:
A feeling of the surroundings spinning or moving,
Nausea or vomiting,
Motion sickness & general unsteadiness,
Lightheadedness & fainting
How to test which ear is affected by BPPV?
Sit up on your bed such that your head hangs over the edge when you lie down.
Turn your head in the right direction & quickly lie down.
Wait a minute before performing the next steps. If you feel dizzy during this time, then it means that your ride sight is affected by BPPV.
If no dizziness occurs, sit up, wait for a while, & repeat the test on the left side.
If you feel dizzy when doing the test on your left side, then that means your left side is the one affected by BPPV.
BPPV Causes:
Inside the ear, lie tiny calcium crystals also called otoconia. Sometimes, these crystals can break from their original position inside the middle ear & deposit inside the semicircular canal of the inner ear.
When this happens, they cause problems with the way the vestibular system located inside the inner ear functions to keep the body’s balance.
These tiny calcium crystals are motion sensitive, thus causing false sensations of motion everytime the patient moves their head in certain ways.
Many actions can trigger the feelings of BPPV. These include:
Rolling over to the side of bed,
Getting in & out of bed,
Bending during yoga,
Tripping your head back during a session at the salon,
Performing any activities that require certain specific head movements
BPPV diagnosis:
In order to provide you with an accurate BPPV treatment plan, your doctor will have to diagnose your condition with precision.
Your doctor will usually ask for a history of your symptoms, & any other illnesses or injuries you have had in the recent past.
Your doctor will also look for any abnormal eye movements, also called nystagmus. Nystagmus is an undeniable physical symptom of Vertigo, which will pretty much seal your BPPV diagnosis.
Your doctor will also check if any of your symptoms occur when you move your head in certain ways & directions, another tell-tale sign of BPPV.
If a physical exam is inconclusive, your doctor might also recommend the Electronystagmus test( the ENG test), &/or the Videonystagmoraphy test( the VNG test), along with the MRI test.
BPPV treatments:
Most cases of BPPV episodes are short-lasting in nature, & go away on their own.
BPPV treatments usually focus on reinstating the misplaced calcium crystals in the inner ear back to their original position.
They do this with the help of certain exercises called the canalith repositioning maneuvers, which help move the displaced calcium crystals back to their original position.
The most common canalith repositioning maneuvers that doctors use to move the displaced calcium crystals back into their original position are:
Epley Maneuver: The Epley Maneuver is a very well-known Vertigo exercise that vertigo specialists recommend for BPPV treatment. The Vertigo exercise involves moving your head in certain directions to help the displaced calcium crystals fall back into their original position.
The Epley Maneuver is known to be very effective when it comes to long-lasting BPPV treatment. It involves a few very simple steps that you can even carry out at home. Although in the beginning, you will be required to perform the Epley Maneuver under the supervision of a Vertigo specialist.
Semont Maneuver: The Semont maneuver takes about 15 minutes to complete, & involves certain specific head movements similar to the Epley Maneuver.
Although it is a bit less common than the Epley Maneuver, it has a wide success rate in BPPV treatment, next only to the Epley Maneuver.
Medicines: BPPV treatment also includes various medications like meclizine, diazepam, dramamine, phenergan, & scopolamine. Patients are supposed to take Vertigo medicines along with performing dizziness & vertigo exercises for effective BPPV treatment.
Surgery: In some cases, surgical interventions may be required for effective & long-lasting BPPV treatment. Doctors will aim to remove the displaced calcium crystals inside the ear with the help of surgical instruments to effectively treat your BPPV symptoms once & for all.
The surgical approach is usually taken when all other BPPV treatment procedures fail, & your BPPV symptoms are getting worse overtime.
Want to know more about BPPV, its signs, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, & prognosis? Visit www.vertigoandearclinic.com.